WHAT IS AN
INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT PROGRAM?
A comprehensive IPM program consists of three phases:
STEP 1:
Planning
- Helps operators understand the extent of their insect problems
- Charts a course to address issues proactively instead of being reactive
STEP 2:
Implementation
- Implement insect control tactics to reduce infestations on your property
- Execute a multi-method approach to insect control
STEP 3:
Evaluation
- Follow up on program effectiveness
- Checking and monitoring on a regular basis
- Reviewing/adapting a program as needed
STEP 1:
PLANNING
1. INSPECT
Inspect operation and find areas with heaviest insect populations.
2. LEARN
Learn the most economical means for minimizing insect infestations and damage through various control measures.
3. SET
Set a threshold where insect populations and environmental conditions dictate that action must be taken.
4. TRAIN
Train your employees on the best mix of tactics in the most important target areas for maximum control.
PLAN YOUR PROGRAM
Set out Starbar® traps inside and around your barns and other facilities to measure the amount of fly activity. This will help you understand the extent of the fly problem, know which target areas to address, and know how to determine the best mix of tactics for maximum fly control for your operation. Perfect for controlling flies on both small- and large-scale operations, Starbar® baits offer superior control of nuisance and disease spreading flies. Their bait matrices encourage flies to feed and can be used in rotation to discourage fly resistance.
WATCH OUR VIDEO TO LEARN MORE ABOUT IPMSTEP 2:
IMPLEMENTATION
To deliver the best results, use an all-encompassing approach to insect control that utilizes cultural, physical, biological, and chemical control efforts.
For example, to protect dairy operations from costly fly infestations, it is important to use a variety of fly traps, fly baits, feed-through fly control and on-animal treatments to manage disease-spreading fly populations. Learn more in our checklist for implementing a fly control program!
-
Cultural
-
Physical / Mechanical
-
Biological
-
Chemical-Conventional
-
Chemical-Biorational
SANITATION IS KEY
Comprehensive insect control begins in the Cultural phase where daily habits are established and best sanitation practices are implemented around the facility.
Hover over images to learn more.
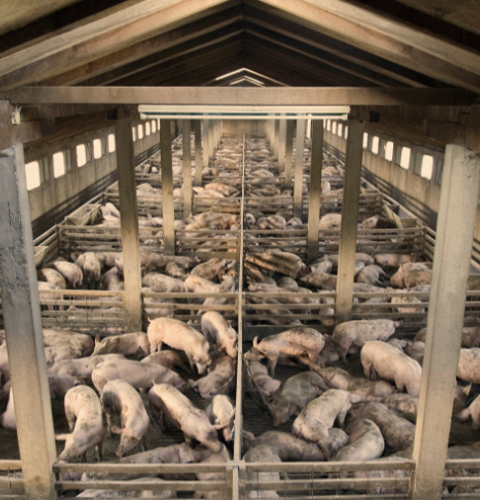

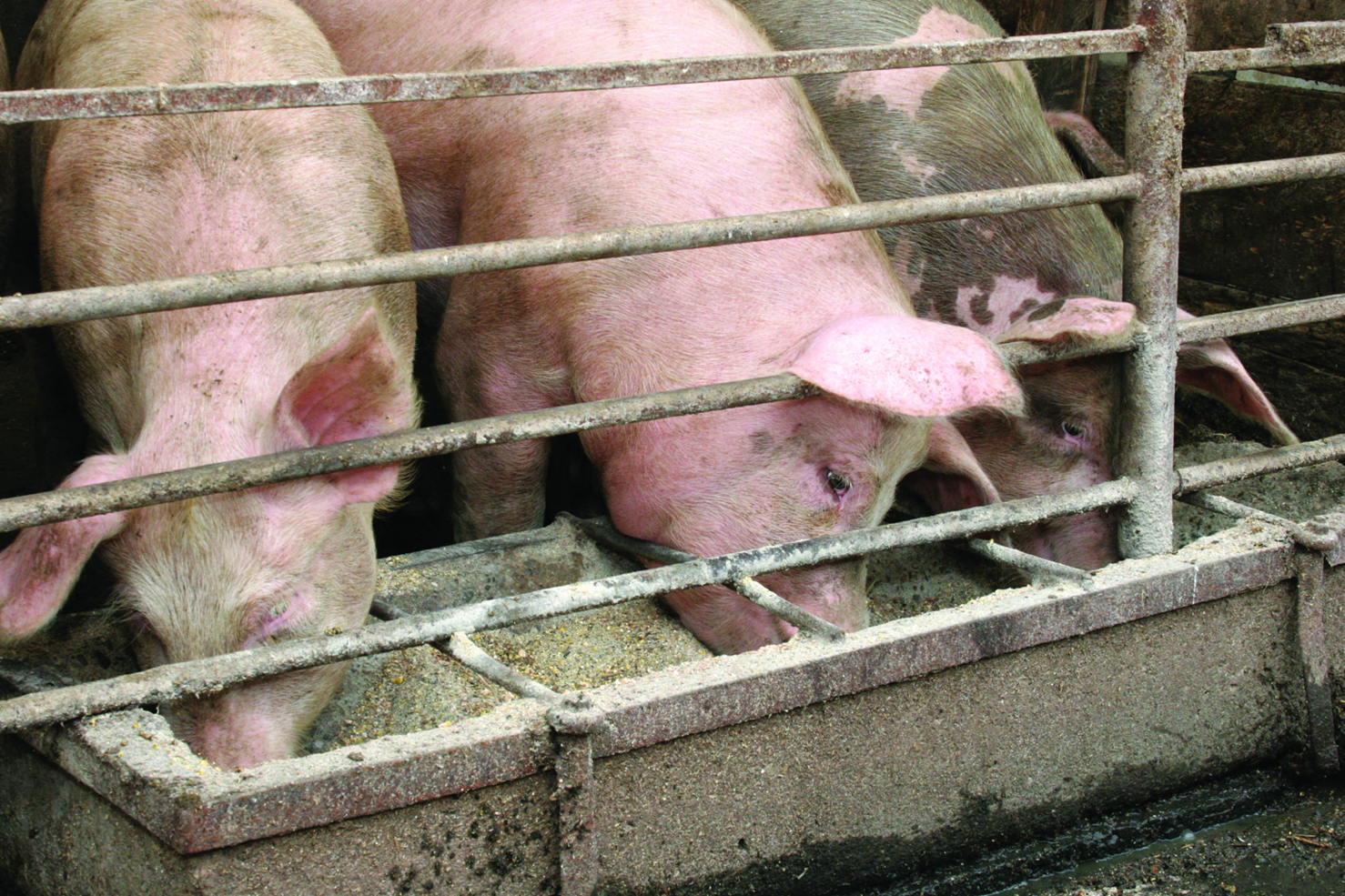
Manage manure in a timely and consistent manner, as it is the primary breeding site for flies. Also, regularly clean spilled milk and feed. In a swine operation, the manure pit needs to be maintained, and the practice of good husbandry skills should be incorporated to prevent organic matter buildup around facilities and equipment.
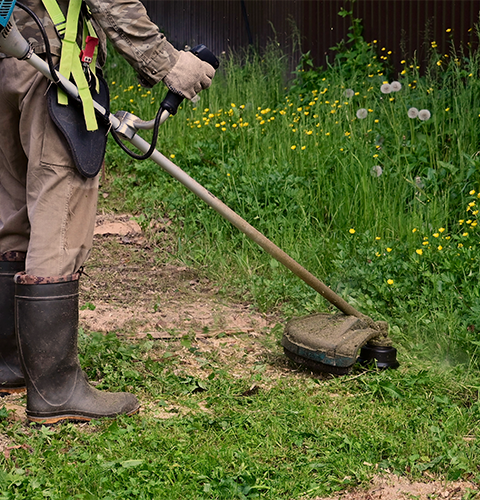

Regularly maintain weeds and tall grasses as they provide an ideal resting place for flies and other insects. On pasture, clear or spread out grass clumps, or mulch when possible.
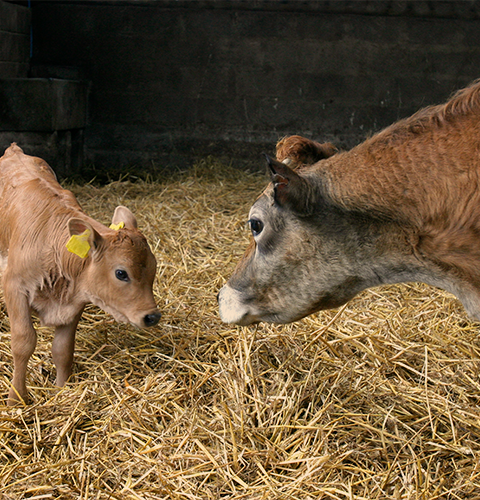

Clean spilled milk and decaying straw and wood shavings in calf bedding, which can also serve as a breeding site for flies and cockroaches.
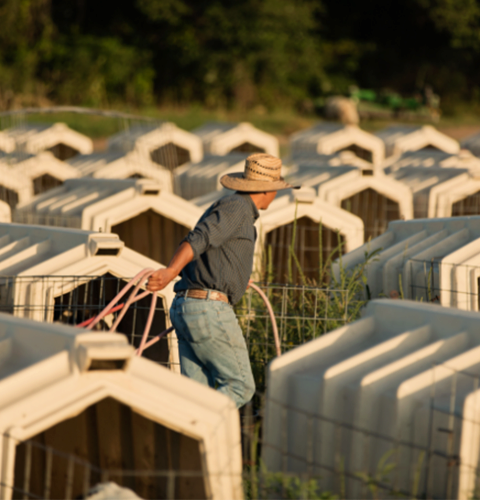

Regularly clean and move calf hutches and pens and keep them well ventilated.




MAINTAIN FARM STRUCTURES
Efforts include the maintenance of all structures and facilities that deny flies, cockroaches and other insects access points and make the areas less hospitable to the pests.
Hover over images to learn more.
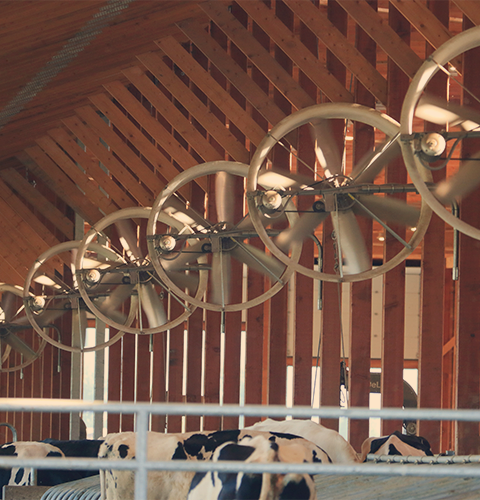

Install fans to produce a downward and outward air flow that can limit fly activity in barns and other enclosed spaces.

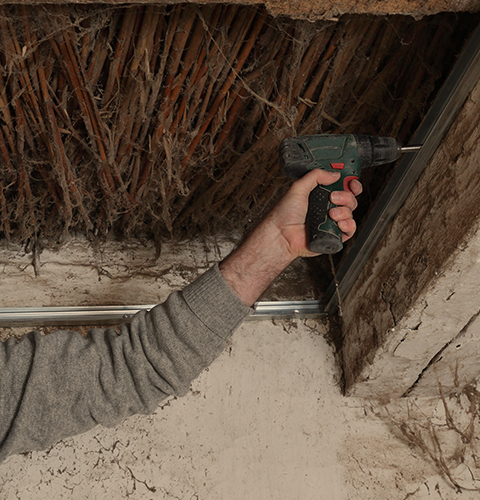
Remove fly and cockroach entry points in physical structures by caulking, filling holes and sealing around electrical outlets.

Patch or seal any cracks or crevices in structures, and secure fine-mesh screens over any windows.
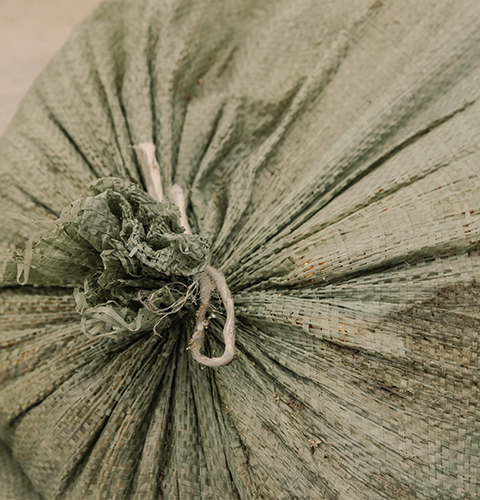

Keep garbage tightly sealed and, ideally, housed in an enclosed area.




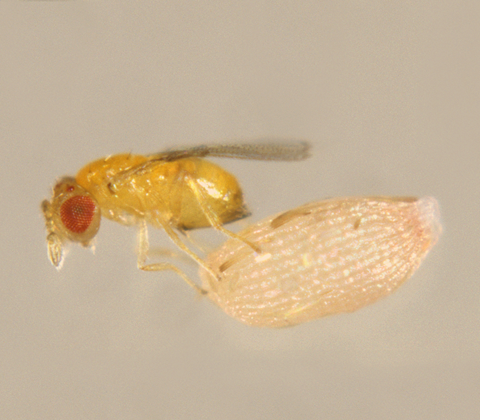
BENEFICIAL PESTS FOR YOUR IPM
Biological control incorporates naturally occurring fly enemies to help keep their populations in check. These beneficial pests can be used as part of an IPM program to maximize fly-control efforts with no adverse effect to animals or humans.
Hover over images to learn more.
ROTATION OF ACTIVE INGREDIENTS
Control adult flies, cockroaches, fire ants, mosquitoes, etc. by incorporating a balanced mix of insect control modes of action throughout the operation, and ensure a rotation of active ingredients to prevent resistance.
Click below to see which products we recommend.
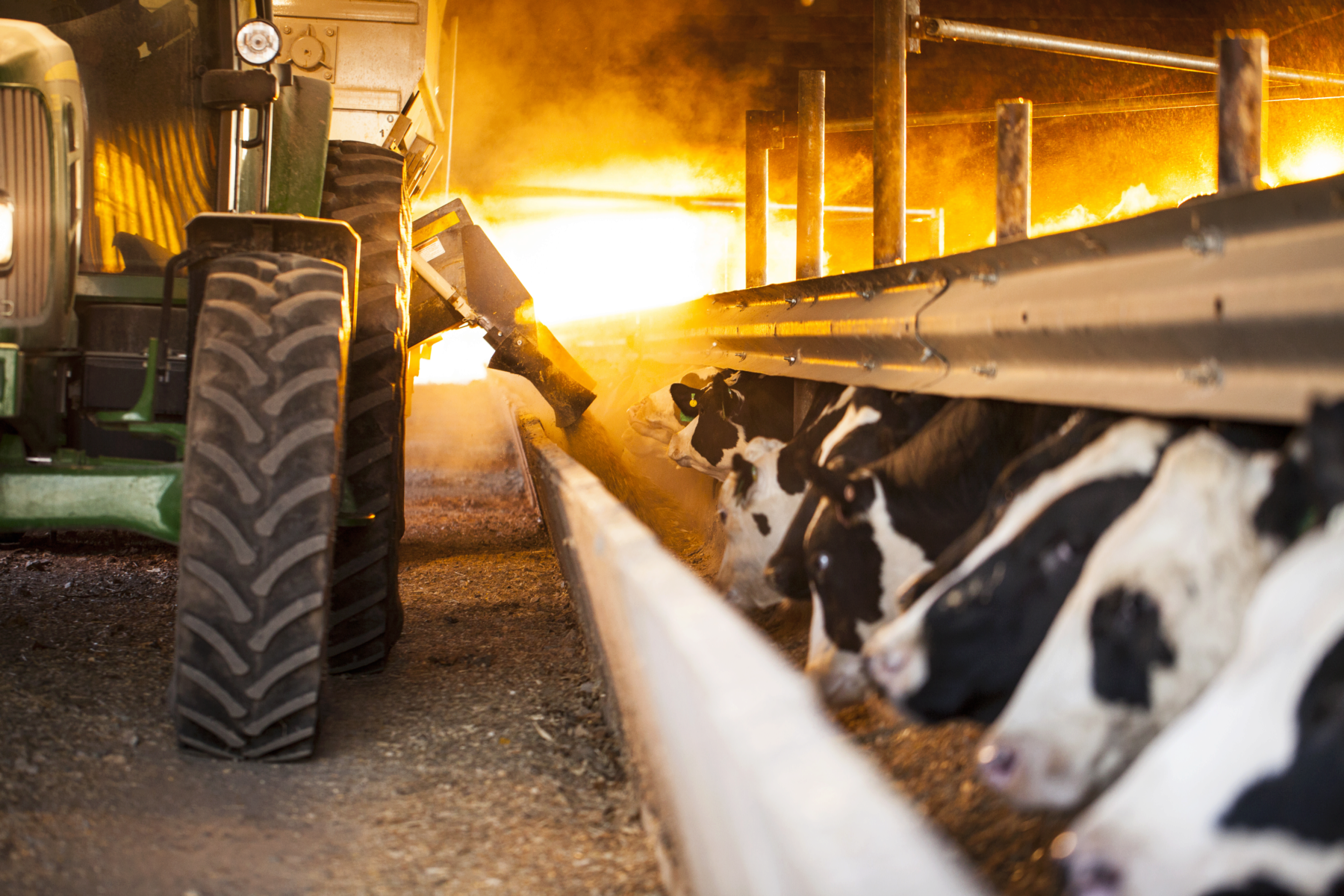
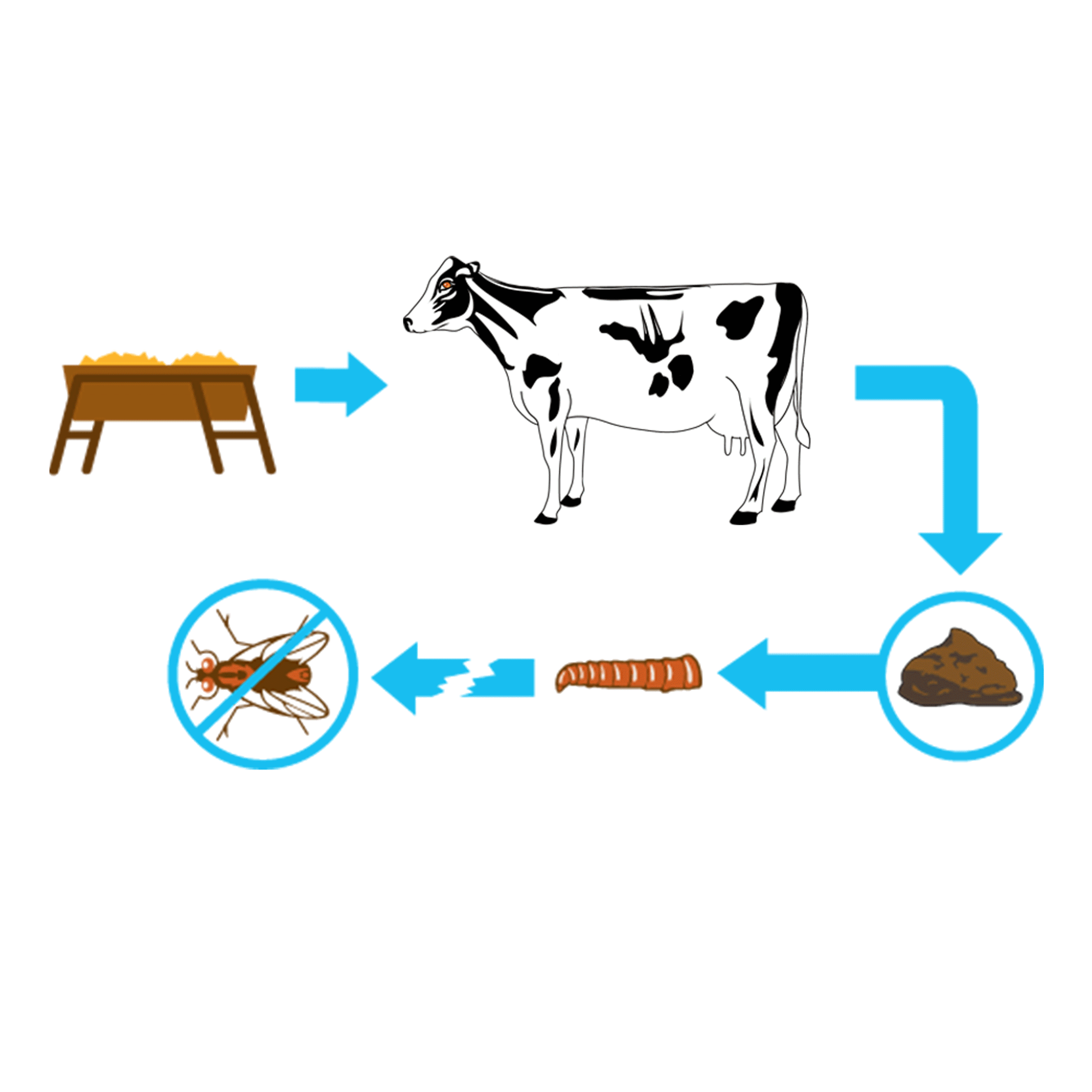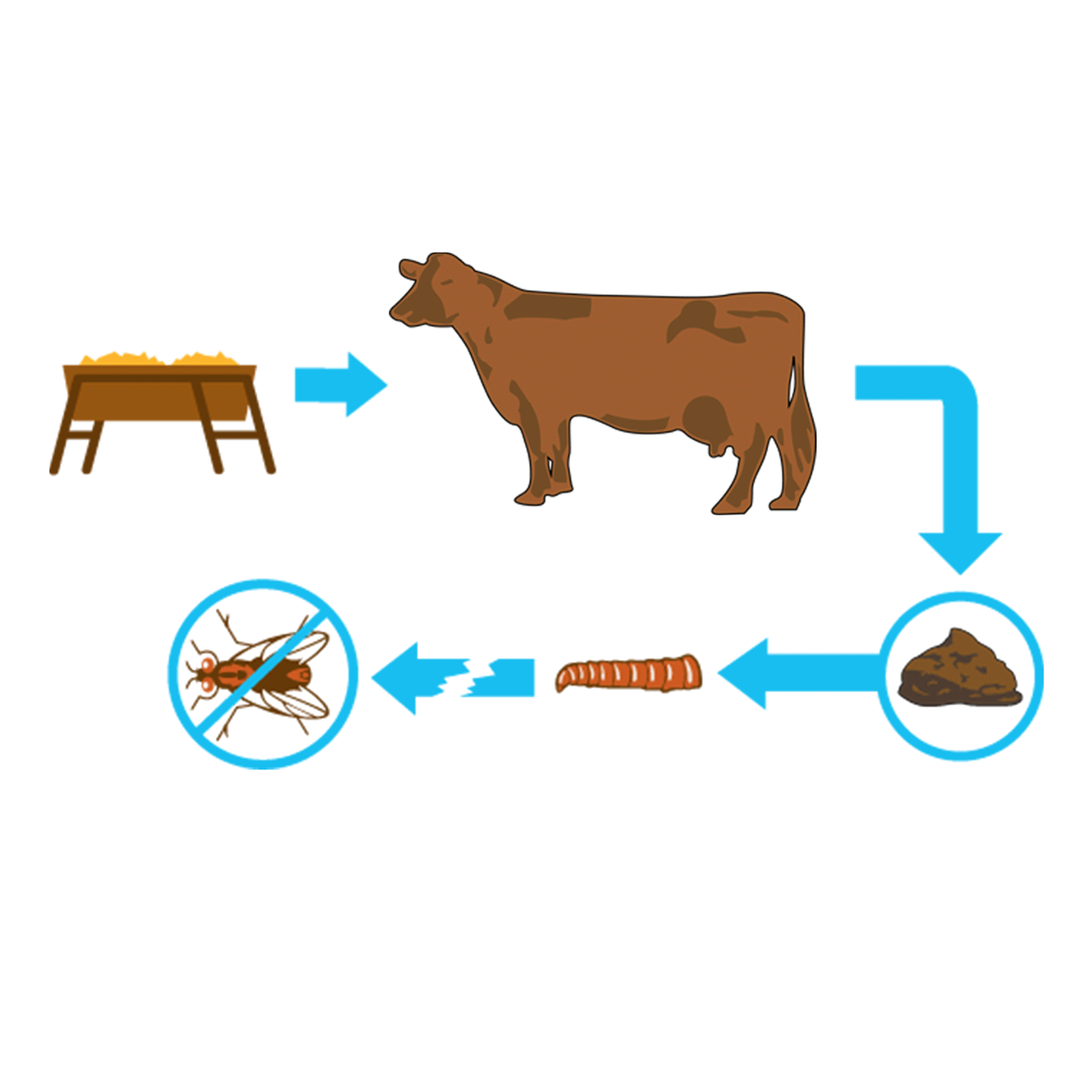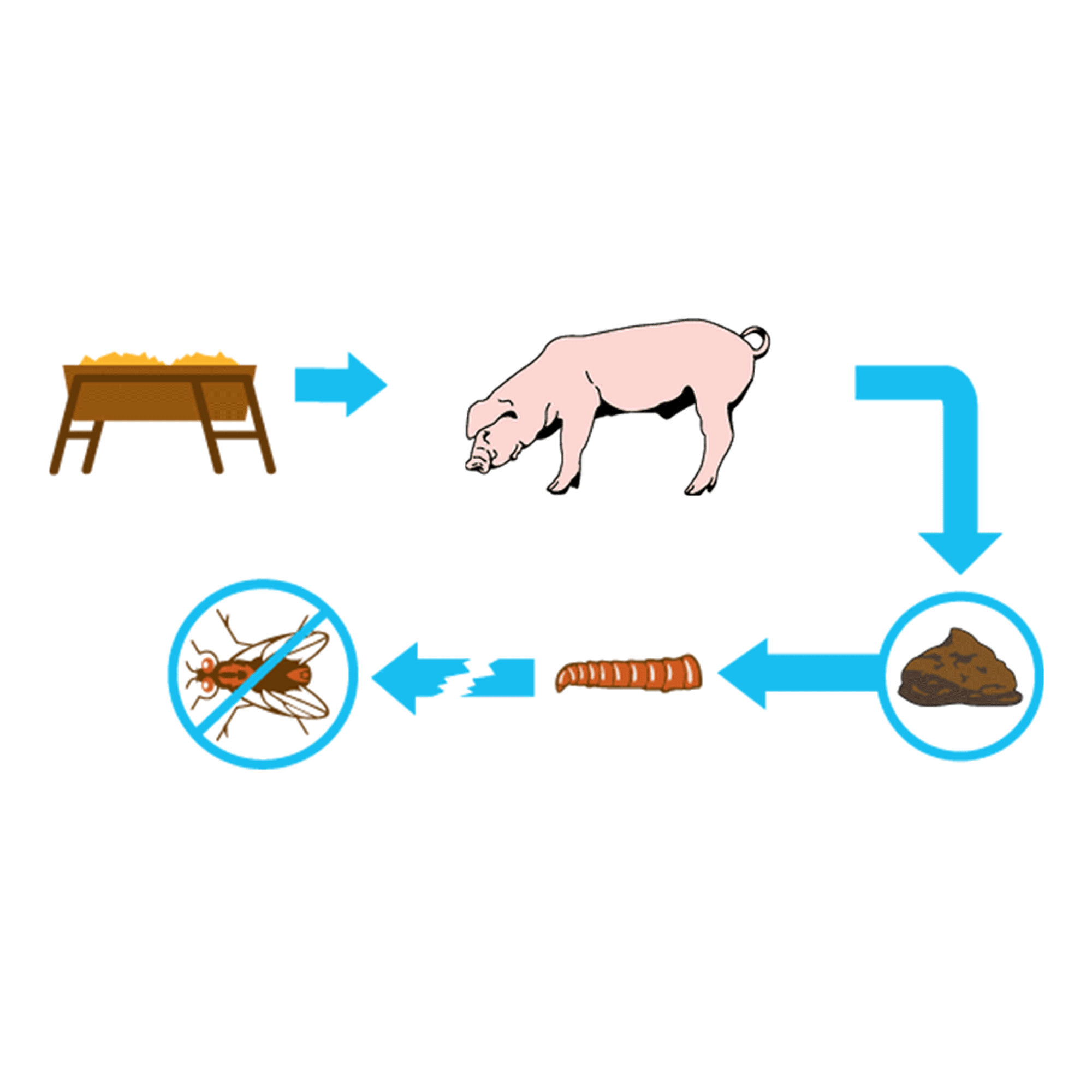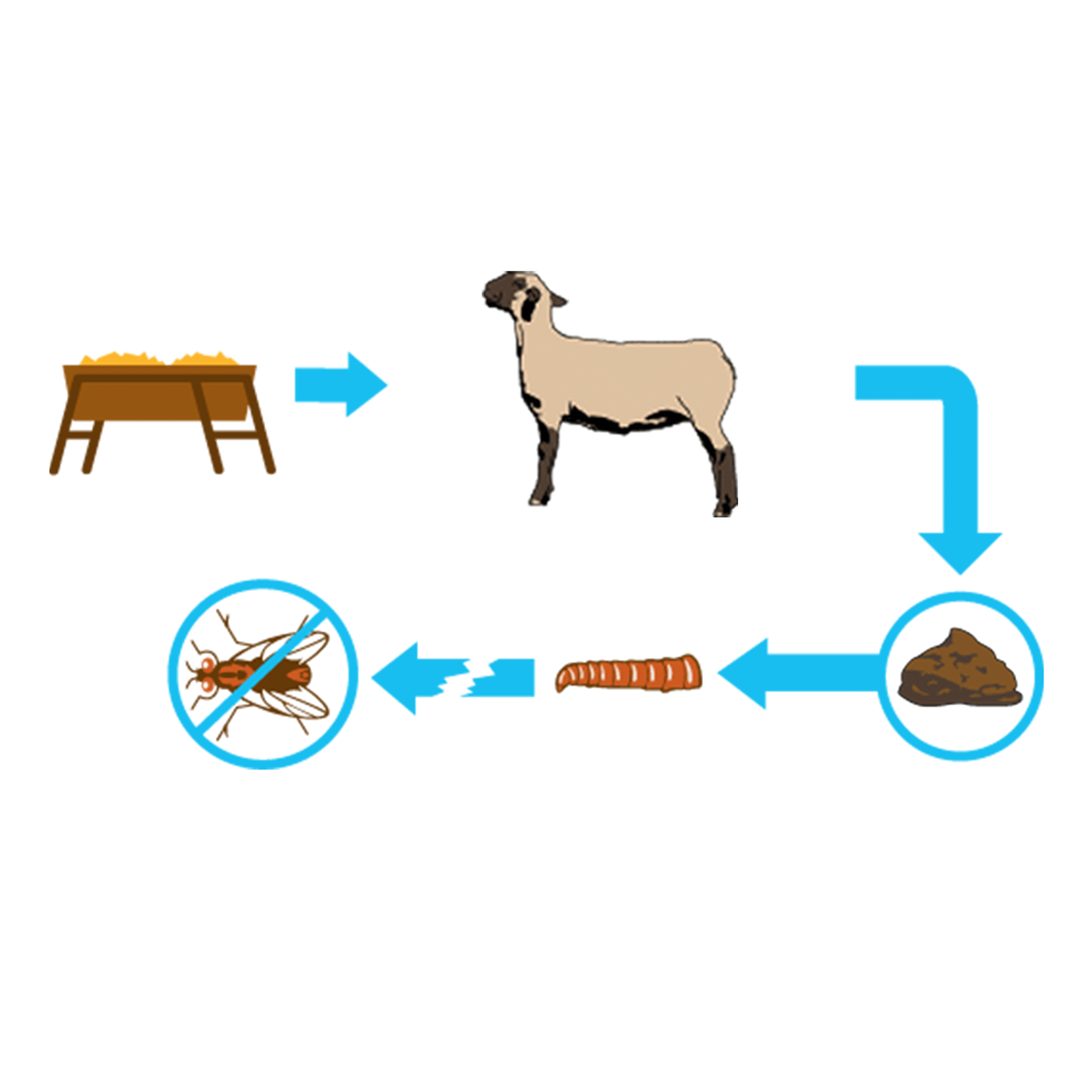
FEED-THROUGH FLY CONTROL
Use the proven feed-through fly control ClariFly® Larvicide. Using ClariFly® Larvicide is simple. As a feed additive, it is simply incorporated into an animal's feed, and that is all the work an employee has to do to help prevent flies. Leave it and forget it. The active ingredient takes care of the rest, as it passes through the digestive system of the animal, and then sits in fresh manure, where flies lay their eggs. The mode of action in the active ingredient prevents house flies, stable flies, face flies, and horn flies from developing into adults, interrupting the life cycles. With ClariFly® Larvicide, you get cost-effective fly control that requires very minimal additional work and effort.
Click on the logos to learn more.
Break the Fly Life Cycle
A 30/30 Program encourages operations using ClariFly® Larvicide to start including in their feed or supplement early in the spring, 30 days before flies begin to appear through 30 days after the first frost when cold weather reduces or ends fly activity. This ensures an ideal window of treatment with the products, protecting against an unpredictably early or late start to the spring or winter seasons.
STEP 3:
EVALUATION
1. TRACK
Track fly population results by using speck cards and traps from Starbar®.
2. ROTATE
Rotate active ingredients to prevent resistance.
3. DOCUMENT
Document the progress, making changes as necessary.
TRACK YOUR RESULTS
After implementing your fly control products, monitor fly populations throughout the operation with the use of speck cards and a variety of traps. It is important to rotate active ingredients to prevent resistance. Document your progress with a concise record of locations, conditions, and actions taken.
WATCH OUR VIDEO TO LEARN MORE ABOUT BAIT ROTATION